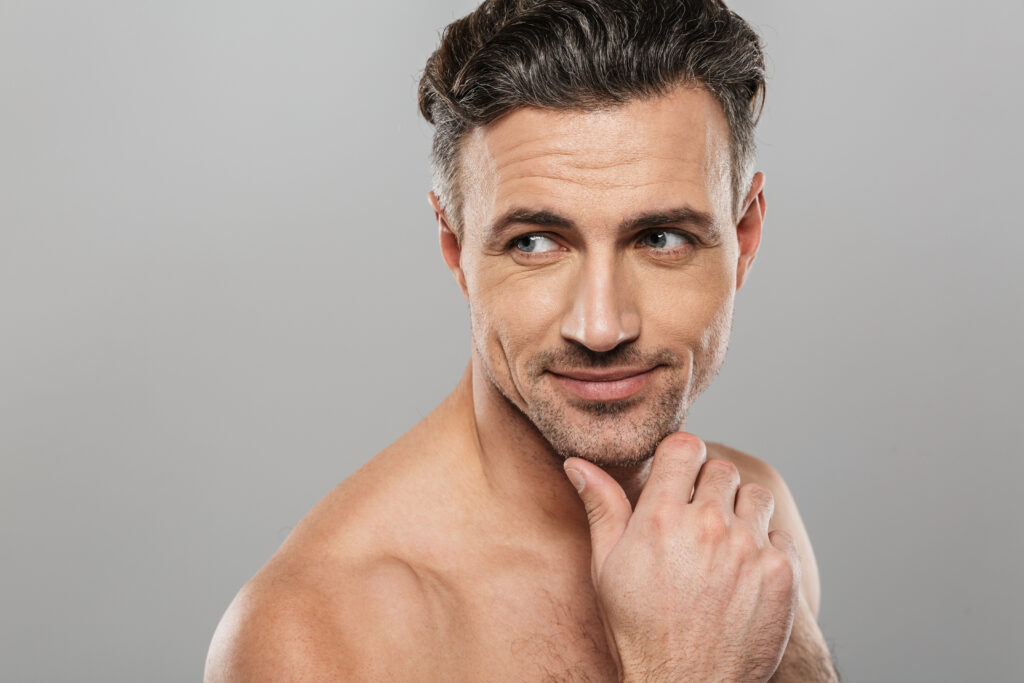
Hereditary male-pattern baldness and female-pattern hair loss or androgenetic alopecia, is a common concern affecting millions of people worldwide. In this blog, award-winning facial plastic surgeon and hair restoration specialist, Dr. Demetri will explore the genetics behind hair loss and how to recognize the early signs of what may be hereditary hair loss, along with insights into treatment options.
The Genetics of Hair Loss
Androgenetic alopecia, commonly referred to as male-pattern baldness in men and female-pattern hair loss in women. This type of hair loss occurs when hair follicles shrink over time due to a genetic sensitivity to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This hormone weakens the hair follicles, leading to thinning hair and eventually baldness.
Causes of Hair Loss: Understanding the Triggers
Understanding the underlying causes can help distinguish between temporary hair loss and more permanent, hereditary hair loss. While genetics is a primary cause, other factors can also contribute to hair loss:
- Hormonal Changes- Hormonal imbalances, such as those caused by pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid problems, can exacerbate hereditary hair loss.
- Medical Conditions- Conditions like alopecia areata, scalp infections, or autoimmune disorders can accelerate hair loss in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Stress and Poor Nutrition- Emotional stress and nutritional deficiencies can weaken hair, although these causes are usually temporary and reversible with proper care and treatment.
Early Signs of Hair Loss: What to Look For
One of the most critical steps in managing hair loss is recognizing the early signs. The sooner you detect hair loss, the sooner you can seek treatment and potentially slow the process.
- Thinning Hair- If your hair feels less dense or you notice more hair shedding in the shower, on your pillow, or in your brush, this could be an early sign.
- Receding Hairline- A slow retreat of your hairline, particularly around the temples, is often one of the first indications of male-pattern baldness.
- Thinning at the Crown- For both men and women, thinning at the crown of the head can signal hereditary hair loss.
Treatment for Hereditary Hair Loss: What Are Your Options?
While genetics are the primary driver of hereditary hair loss, lifestyle factors like maintaining a balanced diet, reducing stress, and using gentle hair care products can support hair health.
If you have a family history of hair loss, taking early action is essential by consulting with a hair loss specialist. Dr. Demetri works with a local pharmacy in order to offer custom medication formulations and performs advanced hair transplantation restoration procedures.
Hair Loss Medication– Medications like minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) are FDA-approved treatments for androgenetic alopecia. These treatments help slow down hair loss and, in some cases, promote hair regrowth.
FUE Hair Transplants– (Follicular Unit Extraction) is a minimally invasive hair restoration procedure. This technique leaves minimal scarring and allows for a quicker recovery compared to traditional hair transplant methods. FUE is highly effective for patients with male-pattern baldness or other forms of hair loss, offering natural-looking results. Many individuals prefer FUE because it delivers a permanent solution to hair loss with minimal downtime.
Hair Loss Evaluation: Schedule a Consultation
If you are concerned about hair loss, we invite you to request an appointment. Early intervention can slow the progression and help preserve your existing hair. Dr. Demetri is a board-certified facial plastic surgeon and hair restoration specialist. For more information visit our website at: Dr. Demetri Hair Restoration or contact us here to schedule a hair loss consultation in Tampa with Dr. Demetri.